Initial Checklist for FortiGate deployment in a Production Environment
In this blog post, we will discuss certain things that should be the first things you check before deploying a FortiGate device in a production environment. Whether you are new to the Fortinet environment or have some experience managing devices, this blog will be helpful for you.
Here is list of few things you should keep in mind.
Device Connectivity to Internet
FortiGate needs to have internet connectivity to validate license and download signatures from Fortiguard database. You need to make sure that you have a default route present in the routing table to route traffic to internet. If device is not connected to internet you may run into issues like webfilter will stop rating websites and affect production environment.
DNS Settings on the FortiGate
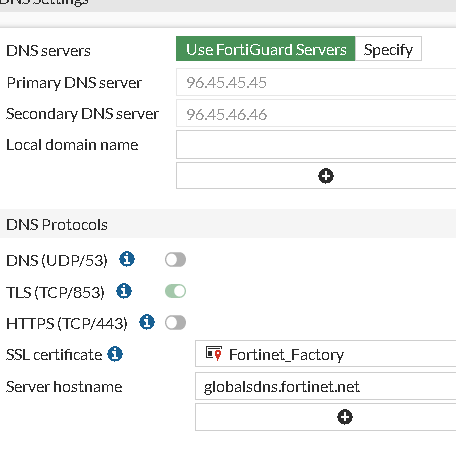
The DNS settings on FortiGate play a vital role in connecting the device to Fortiguard servers. By default, FortiGate is configured to use the default Fortiguard DNS servers. However, from FortiOS 7.0.2 onwards, FortiGate will use DoT (DNS over TLS) servers only for local DNS traffic. You can validate the DNS settings on the CLI using the command show system dns.
As shown in the screenshot below, selecting the default DNS settings uses the servers which support DoT only. DoT works on port 853.
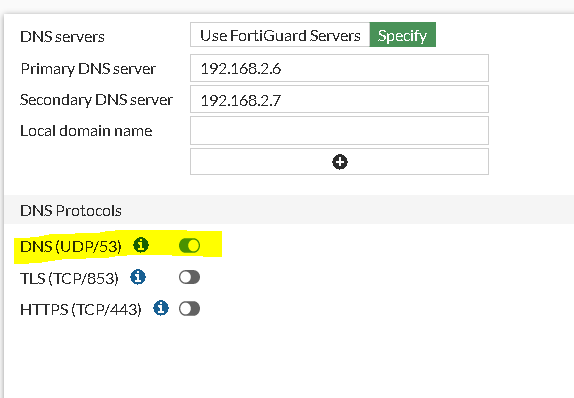
If you want to change the DNS settings to your internal servers for any reason, make sure to change the port to 53 if your servers do not support DoT and operate on port 53.
Ports required by FortiGate
If you have any upstream device make sure below mentioned ports are open
8008: Used by FortiGate to authenticate with FortiGuard when an HTTP override request occurs for FortiGuard web filter HTTP override authentication.8010: Used for HTTPS override requests for FortiGuard web filter HTTPS override authentication.8020: Used for FortiGuard web filter warning authentication.